55503282
Periodensystem der Elemente
In 10 interaktiven H5P-Modulen wird Wissen zum Thema Periodensystem der Elemente eingeübt und anschließend abgefragt.
Das Medium bietet H5P-Aufgaben an, die ohne zusätzliche Software verwendbar sind.
Durch interaktive Aufgabentypen wird das audiovisuelle und interaktive Lernen einfach.
Lernen macht jetzt Spaß!
Included Tasks
- I Entstehung des PSE - interaktive Aufgaben
- II Periodensystem kennenlernen - interaktive Aufgaben
- III Gruppen und Perioden - interaktives Video
- IV Elementkarten beschriften - interaktive Aufgabe
- V Protonen; Elektronen; Neutronen - interaktives Video
- VI Bauplan der Atome - interaktive Aufgabe
- VII Symbole; Namen; Aggregatzustände - interaktive Aufgabe
- VIII Außenelektronen; Schalen; Elemente - Dialogkarten
- IX PSE-Wissen prüfen - interaktive Fragen
- X PSE-Quiz - interaktive Aufgabe
Curriculum-centred and oriented towards educational standards
Matching
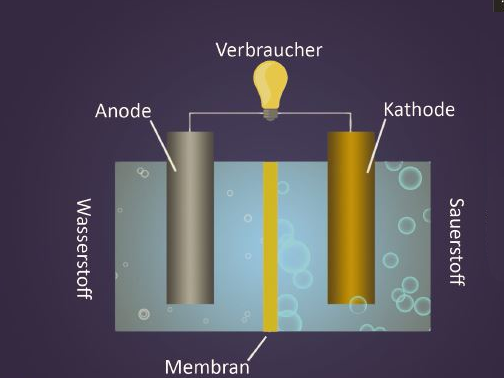
Fuel Cell
A smartphone offers a lot of opportunities nowadays. The numerous apps and applications may enrich your daily life but cost a lot of electricity. It is particularly annoying when the device fails at the most inconvenient moments. Conventional rechargeable batteries are often empty after one day already, and the device needs to be plugged in. Besides many others, also this problem could be solved by using fuel cells – thus considerably increasing the duration of the smartphone.
Periodic Table
With the help of the periodic system chemists can predict properties of chemical elements and derive chemical reactions. But you need not be a chemist to understand the periodic system.