55503683
Redoxreaktionen
In unserem Arbeitsheft Chemie 7, Vol. 1 – Redoxreaktionen finden Sie 50 interaktive und didaktisch aufbereitete Aufgaben.
Das Medium bietet H5P-Aufgaben an, die ohne zusätzliche Software verwendbar sind. Das Medium enthält interaktive Videos und 50 H5P-Aufgaben zum Thema Redoxreaktionen.
Durch interaktive Aufgabentypen wird das audiovisuelle und interaktive Lernen einfach.
Lernen macht jetzt Spaß!
Included Tasks
- 1. Einstieg - Redoxreaktionen - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 2. Oxidation oder Reduktion? - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 3. Oxidation und Reduktion finden gemeinsam statt - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 4. Reduktion und Oxidation - Begriffe Zuordnen - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 5. Verbrennung von Methan - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 6. Redoxreaktionen im Alltag - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 7. Redox und Elektronentransfer - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 8. Schreiben von Halbgleichungen - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 9. Reaktion zwischen Natrium und Chlor - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 10. Reaktion zwischen Chlor und Kaliumbromid - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 11. Was bedeutet Oxidationszahl? - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 12. Oxidationszahlen in Verbindungen - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 13. Oxidationszahlen in Formeln - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 14. Oxidationszahlen in Redoxreaktionen - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 15. Änderungen in Oxidationszahlen - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 16. Chemische Formeln überprüfen - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 17. Redoxreaktionen - Reflexion - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 18. Redox oder nicht? - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 19. Reaktion von Wasserstoff mit Sauerstoff - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 20. Korrosion - Interaktive Aufgabe
- 21. Das Dach des Berliner Doms - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 22. Oxidationszahl 0 - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 23. Finde die Oxidationszahlen heraus! - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 24. Oxidation oder Reduktion? - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 25. Kupfersulfid - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 26. Das Periodensystem und Oxidation - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 27. Redoxreaktionen im engeren Sinn - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 28. Redoxreaktionen im erweiterten Sinn - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 29. Elektronentransfer - Magnesium und Chlor - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 30. Was sind Oxidations- und Reduktionsmittel? - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 31. Oxidations- und Reduktionsmittel im Labor - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 32. Kaliumdichromat: Ein Oxidationsmittel - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 33. Kaliumpermanganat: Ein Oxidationsmittel - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 34. Alkoholtest - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 35. Kaliumiodid - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 36. Finde das Reduktionsmittel - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 37. Finde das Oxidationsmittel - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 38. Chlor und Natriumbromid - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 39. Iod in Algen - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 40. Eisen in den Eisentabletten - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 41. Reaktion zwischen Kohlenstoff und Kupferoxid - Interaktives Video
- 42. Kaliumsalz der Chromsäure - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 43. Silberchlorid - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 44. Die Redoxreihe der Metalle - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 45. Unedle und edle Metalle - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 46. Metalle im Wettbewerb - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 47. Welches Metall ist reaktiver? - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 48. Magnesium und Kupferoxid - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 49. Verkupfern - Interaktive Aufgaben
- 50. Die Redoxreihe rekonstruieren - Interaktive Aufgaben
Curriculum-centred and oriented towards educational standards
Matching
Aluminium II
The metal aluminium is growing in importance because of its specific properties and manifold application possibilities. This DVD deals with the industrial production of aluminium as a raw material, its processing and the manufacturing of alloys for the finished product. Starting with the raw material aluminium oxide the functioning of an electrolytic cell is demonstrated and explained. Alumina, white and powdery, is melted with great expenditure of energy, and by means of electrolysis converted into aluminium with a degree of purity of 99.9%. As aluminium oxide would not melt before a temperature of over 2,000°C is reached, the mineral cryolite is used as a solvent. The various alloys change the properties of aluminium and are produced according to precise formulations. The alloy is cast into blocks and bars that serve as primary material for processing plants. The responsible handling of resources underscores the importance of recycling. Aluminium is resilient and versatile.
Solutions, Emulsions and Mixtures of Substances
Be it milk in a cereal bowl, tea in a glass or the air around us. We constantly come across mixtures of substances in our everyday lives. As the name suggests, they are mixtures – mixtures of several so-called pure substances.
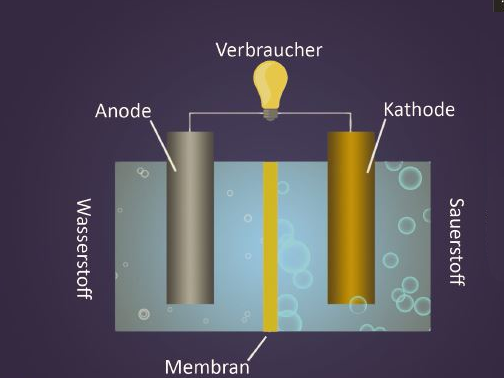
Fuel Cell
A smartphone offers a lot of opportunities nowadays. The numerous apps and applications may enrich your daily life but cost a lot of electricity. It is particularly annoying when the device fails at the most inconvenient moments. Conventional rechargeable batteries are often empty after one day already, and the device needs to be plugged in. Besides many others, also this problem could be solved by using fuel cells – thus considerably increasing the duration of the smartphone.